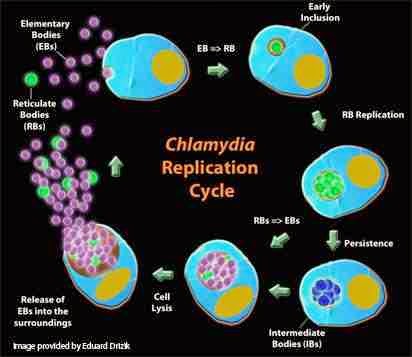
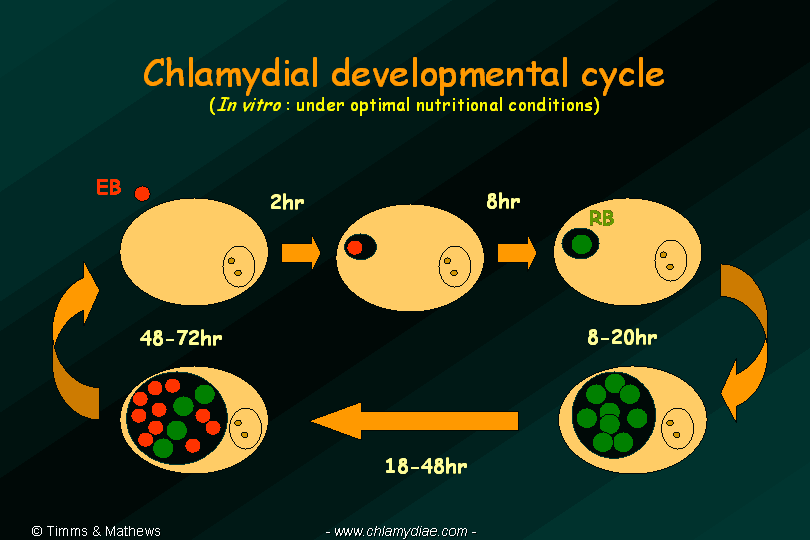
chlamydia diagnosis 
The diagnosis of genital chlamydial infections evolved rapidly from the 1990s through 2006. Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT), such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), transcription mediated amplification (TMA), and the DNA strand displacement amplification (SDA) now are the mainstays. NAAT for chlamydia may be performed on swab specimens sampled from the cervix (women) or urethra (men), on self-collected vaginal swabs, or on voided urine. NAAT has been estimated to have a sensitivity of approximately 90% and a specificity of approximately 99%, regardless of sampling from a cervical swab or by urine specimen. In women seeking an STI clinic and a urine test is negative, a subsequent cervical swab has been estimated to be positive in approximately 2% of the time.
At present, the NAATs have regulatory approval only for testing urogenital specimens, although rapidly evolving research indicates that they may give reliable results on rectal specimens.
Because of improved test accuracy, ease of specimen management, convenience in specimen management, and ease of screening sexually active men and women, the NAATs have largely replaced culture, the historic gold standard for chlamydia diagnosis, and the non-amplified probe tests. The latter test is relatively insensitive, successfully detecting only 60–80% of infections in asymptomatic women, and often giving falsely positive results. Culture remains useful in selected circumstances and is currently the only assay approved for testing non-genital specimens.
How do I know if I have chlamydia?
Most people who have chlamydia have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they may not appear until several weeks after you have sex with an infected partner. Even when chlamydia causes no symptoms, it can damage your reproductive system.Women with symptoms may notice
- An abnormal vaginal discharge;
- A burning sensation when urinating.

- A discharge from their penis;
- A burning sensation when urinating;
- Pain and swelling in one or both testicles (although this is less common).

- Rectal pain;
- Discharge;
- Bleeding.
References
- "www.chlamydiae.com (professional) - Taxonomy diagram". Retrieved 2007-10-27.
- Chlamydia fact sheet from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Thylefors B, Négrel AD, Pararajasegaram R, Dadzie KY (1995). "Global data on blindness". Bull World Health Organ 73 (1): 115–21. PMC 2486591. PMID 7704921.
- Resnikoff S, Pascolini D, Etya'ale D, Kocur I, Pararajasegaram R, Pokharel GP, Mariotti SP (2004). "Global data on visual impairment in the year 2002". Bull World Health Organ 82 (11): 844–851. doi:10.1590/S0042-96862004001100009. PMC 2623053. PMID 15640920.
- Belland R, Ojcius DM, Byrne GI (2004). "Chlamydia". Nat Rev Microbiol 2 (7): 530–1. doi:10.1038/nrmicro931. PMID 15248311.

































I was diagnosed as HEPATITIS B carrier in 2013 with fibrosis of the
ReplyDeleteliver already present. I started on antiviral medications which
reduced the viral load initially. After a couple of years the virus
became resistant. I started on HEPATITIS B Herbal treatment from
ULTIMATE LIFE CLINIC (www.ultimatelifeclinic.com) in March, 2020. Their
treatment totally reversed the virus. I did another blood test after
the 6 months long treatment and tested negative to the virus. Amazing
treatment! This treatment is a breakthrough for all HBV carriers.